The OBC Dicta

The OBC Dicta (or, The Nine Commandments for Peak Performance In Cycling). *** I wrote the first version of this over twenty years ago, hoping that it would become the foundation for another book, but life and acceleration got in the way, and I just found it again in my Google Drive. A ‘Dicta‘ is […]
Vo2Master Vo2Max Value Affirms Garmin Vo2Max Estimator

Vo2Master’s Vo2Max Value Was 98% Consistent with Garmin In May of this year, I wrote a post about the Garmin Vo2Max Calculator. In July, I was able to test my Vo2Max at OBC Headquarters, to compare values. I performed a Graded Exercise Test, using the Vo2Master app. This app, on a cell phone, trapped data […]
DFAA-1 On a BIG SCREEN!
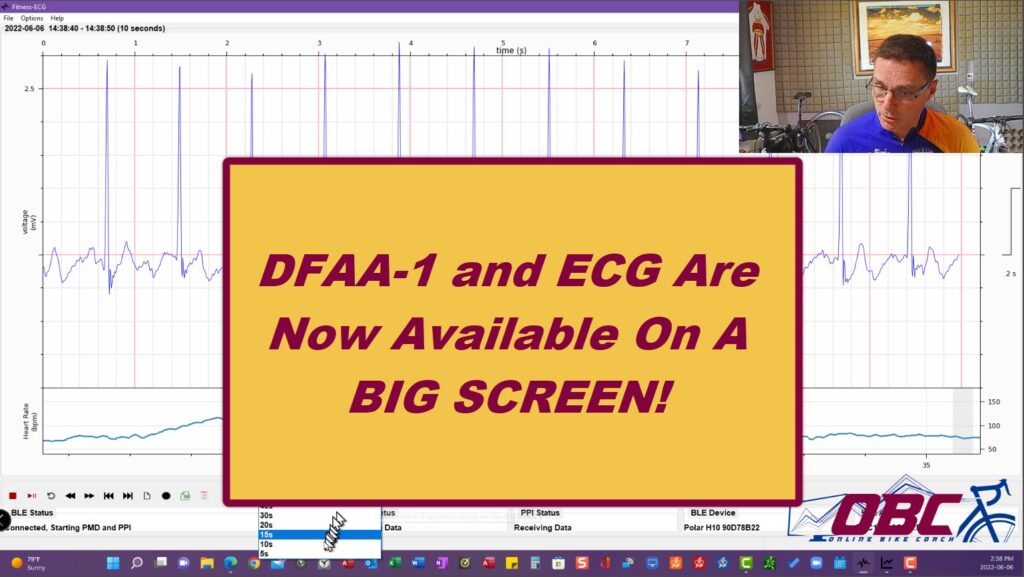
DFAA-1 with ECG is Now Available On a BIG SCREEN! I’ve been working with two professionals now for several months on a project, and we are ready to start releasing it in ALPHA. DFAA-1 (Detrended Fluctuation Analysis – Short Term Variable #1) is a way to look at Heart Rate Variability and Cardio-Vascular Health. Dr. […]
Getting FatMaxxer On the Same Screen As PerfPro Studio
The FatMaxxer App for Android is one of my favorite instruments when used in conjunction with a Polar H10 Chest Strap.
More DFAA1 Files From Myself and my Clients
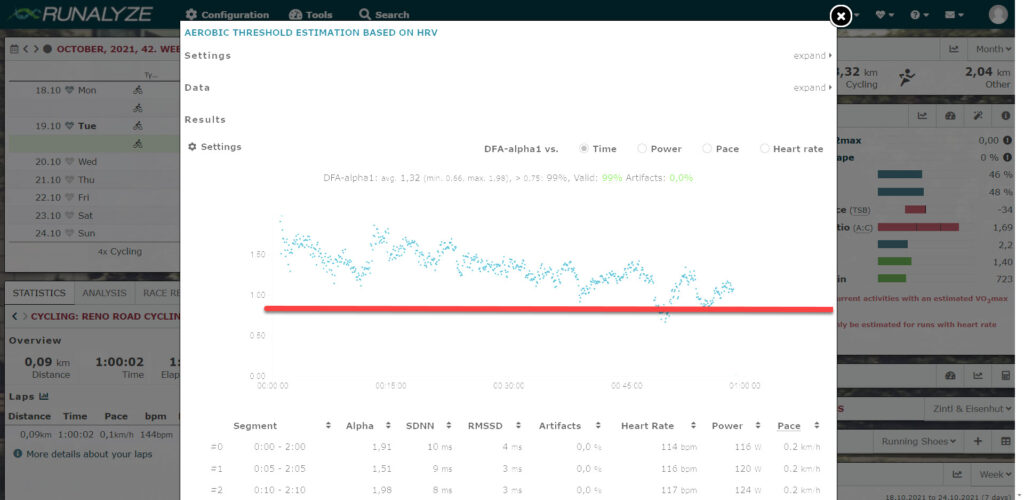
My Own Sleep Was Not Great, But Things On the Cardio Side Are Really Looking Good Well, once again, I didn’t sleep great last night. I woke up around 1:00am, and was up for about an hour. There is stress at the house with a relative, and that may have contributed. Last night, however, I […]
First Night With A “Pink Noise” Generator
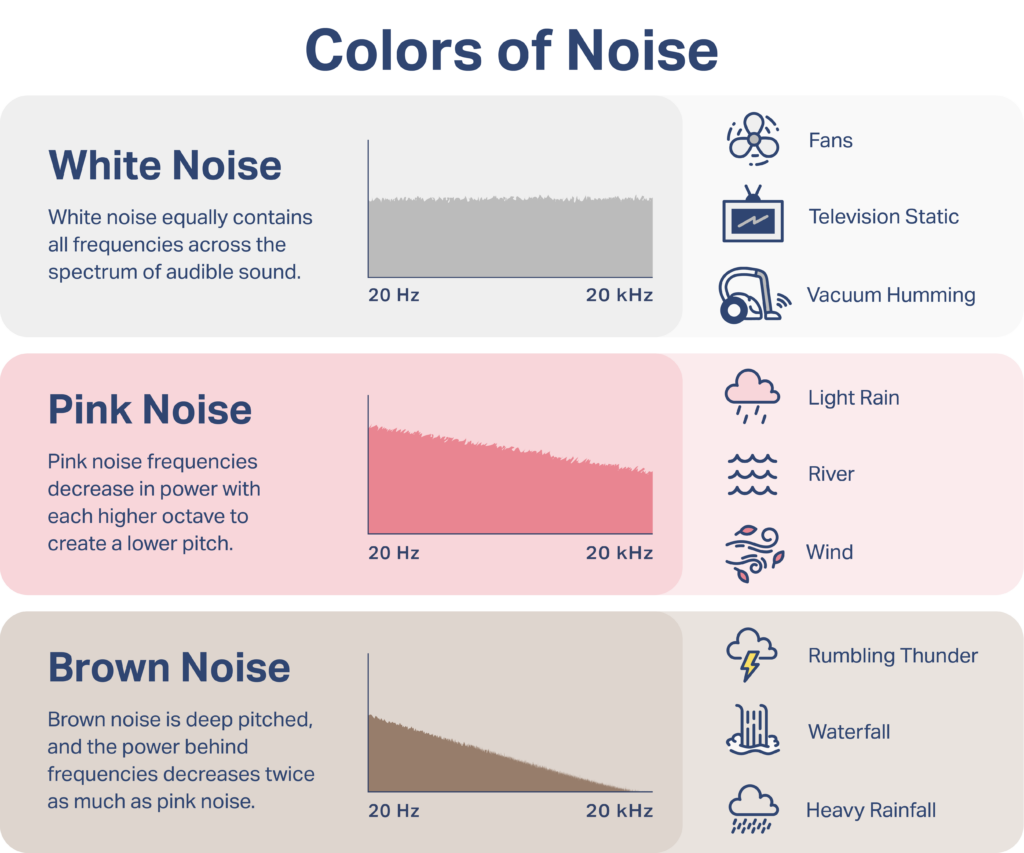
It Was Not the Best Night, But the Time Spent Actually Sleeping With Pink Noise Was VERY Enlightening… I thought I did everything right. Well, almost everything. The one thing I didn’t get around to yesterday was a ride. Instead, I worked on a project for my father, and got a call about some Drone […]
October 9 2021 Post-Ride Analysis
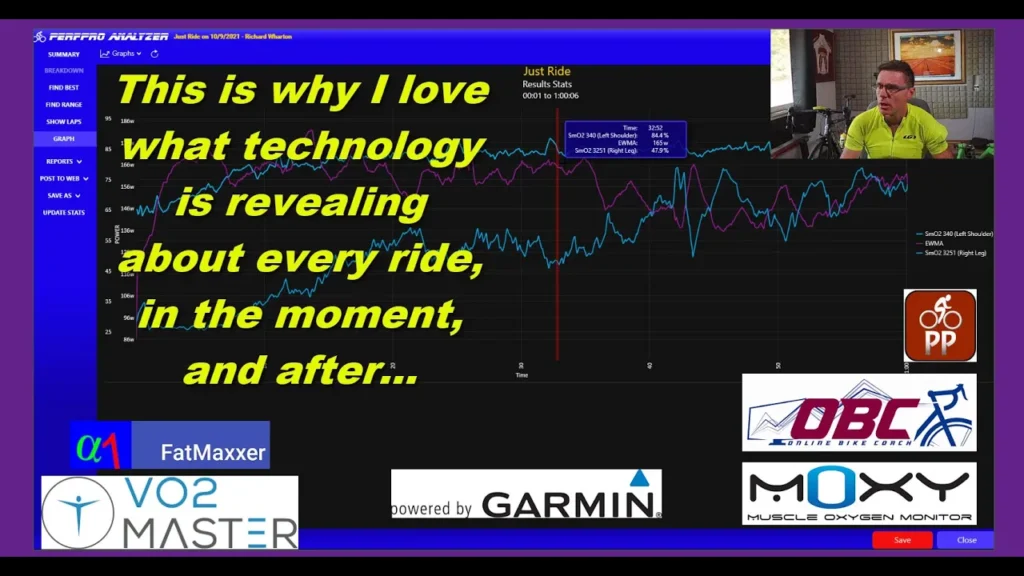
Bouncing Between DFAA1 0.75 and 1.00 for Optimal Fat Burn and Aerobic Base Improvement Having the FatMaxxer Android software on-screen in realtime has brought a new element to my base training. I use the screen to try and keep my intensity between DFAA 1.00 and 0.75. The advantage to this is that I can […]
Let’s Start With An Assessment!

What Is My Current Fitness? Stress is a horrible psychological state. It’s also chemical, and physical. Strain is the actual, physical manifestation of Stress. Think about it this way; Stress is your body, mind, and heart, looking at a hill, and saying… “I have to go climb THAT?!” And Strain is the actual GRIND as […]
Xert Breakthrough With Physiological Metrics
Xert Is On Board With Some Serious Physiological Observations My Client, Dusty, achieved an Xert Breakthrough while I observed his Physiological Metrics. This is Part 2 of what will now be a 3-part series of videos. In Part 1, I described the physiological phenomena behind a good warmup. Today, we’re going to show how Xert […]
Xert Breakthrough With Physiological Metrics Part One – Warmup

We Use a Moxy Monitor, a Vo2 Master, PerfPro Studio, and Xert To Show a PROPER Warmup I continue to learn something almost daily when it comes to mixing Physics and Physiology. The data that we get and use for wattage training, is almost always complemented by the information I collect from physiology. We have […]
